Mykorrhiza Forschung
Aktuelle Berichte über Mykorrhiza
14. Mai 2015
Mykorrhiza steigert Wachstum,
Nährstoffaufname und Salztoleranz von Oliven
Der Olivenbaum (Olea europaea) gilt als sehr robust und anspruchslos. Doch die zunehmende Versalzung von Ackerland reduziert Wachstum und Ernteerträge. Durch die Hitze verdunstet die Feuchtigkeit aus dem Boden, was zurückbleibt, sind Mineralien. Die gezielte Beimpfung von Olivenbäumen mit Mykorrhiza kann die negativen Effekte auf die Pflanze umkehren. Mit Mykorrhiza wird das Wurzelwachstum um mehr als 400 % gesteigert.
The way nature fertilizes itself!
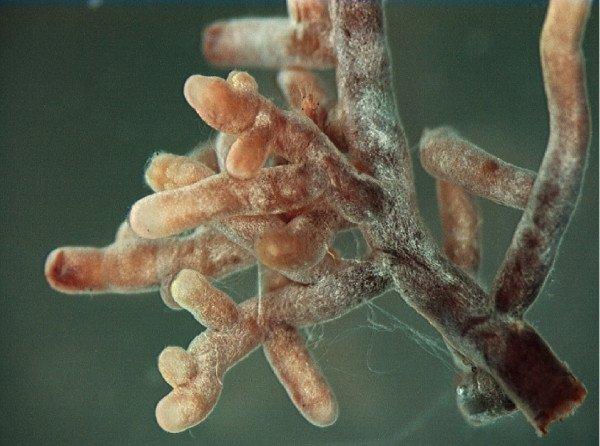
Mycorrhizal fungi are specialised to colonize the root system of plants. A fine network of mycelium covers the roots. This extends their surface area and increases the absorbing capacity of the roots relating to water and nutrient supply and protects the plant from disease.
This is to say that plant roots in symbiosis with mycorrhizal fungi are more effective in the absorption of nutrients and water than the roots by themselves. Find out more about mycorrhiza and how your plants and crop yield will benefit from this relationship!
Types of mycorrhizal fungi
Ectomycorrhiza
Ectomycorrhizas are the most common species in the woodlands of Central Europe. These fungi form a compact sheath of mycelium filaments on the surface of the roots. The mycelium hyphae of ectomycorrhiza don´t penetrate the root cells, but develop a network in extracellular space.
Endomycorrhiza
These are mycorrhizas whose hyphae enter into the plant cells, producing structures that are either balloon-like (vesicles) or dichotomously-branching invaginations (arbuscules).
List of plants that benefit from this symbiosis
An example list of plants that engage into a symbiosis with Mycorrhizal fungi.
Acacia, Agapanthus, Alder (Endo/Ecto), Alfalfa, Almond, Apple, Apricot, Artichoke, Ash, Asparagus Aspen(Endo/Ecto) Avocado, Bamboo, Banana, Barley, Basil, Bayberry, Beans,all Beech, Begonia, Black Cherry, Blackberry, Black Locust, Blue Gramma, Buckeye, Bulbs, all Cactus, Camellia, Carrisa, Carrot, Cacao, Cassava Ceanothus Cedar, Celery, Cherry, Chrysanthemum, Citrus, all Clover, Coconut, Coffee, Coral Tree, Corn, Cotton, Cottonwood...
Tips and products
Useful application tips and informations on Mycorrhiza products.
Agriculture: Available Phosphorus and Mycorrhiza Inoculation:
High levels of available phosphorus (at the time of inoculation) do not harm the mycorrhiza, but they can slow down the germination process. One of the main functions of mycorrhiza is to extract phosphorus from the soil. If there is already a high level of phosphorus available to the plant, the mycorrhizas tend be slower or lazier, so to speak, they have no reason to get to work. When inoculating with mycorrhiza it is best to keep the available phosphorus levels around a more natural level.